It could be a sign of gout if you’re experiencing sudden joint pain, redness, and swelling. Gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, which can limit your abilities and cause pain. Fortunately, gout is treatable. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the symptoms, causes, treatments, and prevention measures for gout. Additionally, we’ll explore how lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can help manage the condition. Lastly, we’ll answer whether gout can be cured entirely or not. Keep reading to learn more about this condition and how to treat it effectively.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Gout: An Overview
- Identifying the Gout Symptoms
- Causes Behind Gout1.
- Available Treatments for Gout
- Diagnosing Gout: What to Expect
- Preventing Future Gout Attacks
- Can Gout Completely Be Cured?
- What does the number say?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
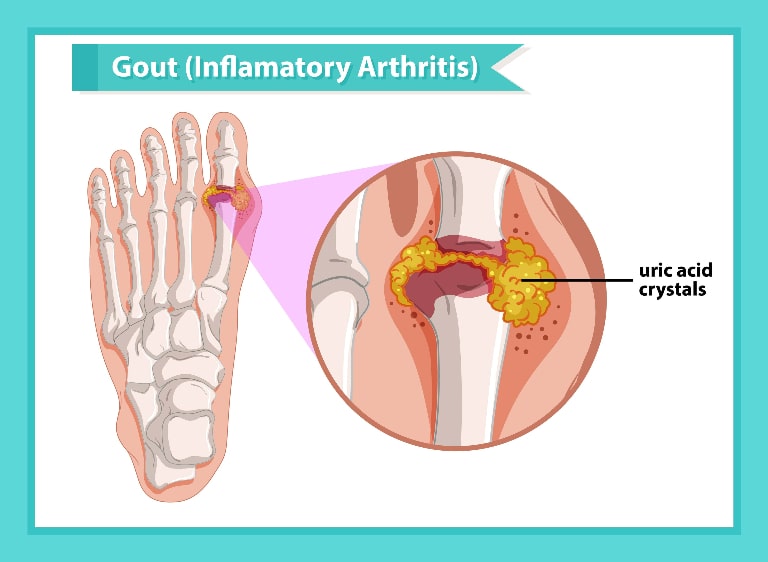
1. Understanding Gout: An Overview
Gout, a type of arthritis, arises from high uric acid levels. Uric acid crystals accumulating in joints result in severe pain. This waste product forms from purine breakdown. If left untreated, gout can harm joints and lead to kidney stones. Lowering uric acid levels is crucial to prevent future attacks. Early diagnosis of gout is essential to prevent chronic conditions such as kidney disease and other health problems.
2. Identifying the Gout Symptoms
Gout attacks last a week or two and can occur suddenly, causing severe pain & swelling. Symptoms affect the big toe joint & include redness, warmth, and tenderness. Chronic gout may involve persistent joint pain. Experts recommend starting therapy for frequent or brutal attacks or gout with a kidney stones history. After an attack, the affected joint should return to normal, but treatment is crucial to prevent persistence.
3. Causes Behind Gout
The causes of gout include genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions. Factors such as family history, diet, and weight can increase the likelihood of developing gout. Additionally, high blood pressure and metabolic syndrome play a role in its development. Diabetes can also lead to elevated levels of uric acid, which worsens the symptoms of gout. In order to effectively manage or prevent gout, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and weight is of utmost importance. It is also essential to consult a medical professional for any underlying conditions.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to High Uric Acid Levels
Dietary habits such as consuming purine-rich foods like red meat, seafood, alcohol, and sweetened drinks can lead to elevated uric acid levels in the body. In addition, research conducted in 2008 found a connection between high fructose intake and gout; thus, obesity and excess weight can increase the risk of gout.
Furthermore, alcohol consumption, particularly beer, is also linked to gout flares. Other factors that can elevate uric acid levels include sedentary lifestyles, poor hydration, and medical conditions such as kidney problems. It’s important to note that controlling these lifestyle factors can help manage gout symptoms and prevent future flare-ups.
4. Available Treatments for Gout
Gout attacks are treatable, particularly for those with lower than 6 mg/dL blood uric levels. Applying an ice pack or cold compress to the affected joint for 15-20 minutes several times daily can help manage symptoms. Uric acid-lowering medications aim to reduce uric acid levels, and treatment plans are tailored to address symptoms and prevent future attacks, often involving lifestyle changes and medications. Effective gout treatment requires a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers.
Medications Used in Gout Treatment
Gout medications work in two ways: they reduce pain and inflammation and prevent future attacks by lowering uric acid levels. There are different types of medications for gout, such as Allopurinol, colchicine, NSAIDs, and corticosteroids. Allopurinol reduces uric acid levels, while colchicine relieves pain and inflammation. NSAIDs like indomethacin help manage pain and inflammation, whereas corticosteroids relieve severe symptoms. To ensure effective treatment of gout, it is essential to understand how these medications work and their potential side effects. Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on medication selection and dosages.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Gout
Managing a healthy weight is paramount in controlling gout and reducing the risk of flare-ups. To manage symptoms, it is essential to avoid consuming sugary drinks, excessive alcohol, and foods high in purines. Regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and yoga, can help maintain joint flexibility and overall well-being. Stress management techniques like meditation and deep breathing exercises can also be beneficial in controlling gout symptoms.
Foods high in purines, like organ meats, seafood, red meat, and alcohol, can trigger gout attacks. Thus, individuals with gout should opt for foods low in purines to control their symptoms effectively. Additionally, making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and maintaining a balanced diet can lower the risk of developing gout or worsening its symptoms. Seeking medical attention if experiencing severe pain or inflammation is crucial to prevent long-term damage to joints or organs affected by gout.
Further Reading:
- Best Meats to Eat for Gout: A Comprehensive Guide
- Best Drinks for Gout: Your Ultimate Guide
5. Diagnosing Gout: What to Expect
Diagnosing gout involves thoroughly examining the affected joints and testing blood and joint fluid. Healthcare providers measure uric acid levels in the body and look for uric acid crystals, which are indicative of gout. X-rays can also reveal any damage the condition may have caused over time. A complete medical history is also essential to determine any underlying conditions or medications that may contribute to the development of gout. Early diagnosis and treatment of gout can help manage symptoms and prevent further complications such as joint damage or kidney stones.
The Role of Blood Tests in Diagnosis
Diagnostic tests play an important role in confirming the presence of gout and measuring uric acid levels. These tests include blood tests, joint fluid analysis, and imaging studies. Blood tests are crucial in tracking uric acid levels, a significant indicator of gout. They not only aid in diagnosis but also help in managing the condition. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor any changes in uric acid levels over time, essential for proper gout diagnosis and treatment planning. Joint fluid analysis involves removing a fluid sample from the affected joint and examining it under a microscope for urate crystals, another hallmark of gout. Imaging studies like X-rays or ultrasounds can also help detect gout-related joint damage or rule out other conditions with similar symptoms. Combining these diagnostic tests can provide a more accurate diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment for patients with suspected gout.
6. Preventing Future Gout Attacks
Effective management of gout involves reducing risk factors to prevent future attacks. Lowering seafood intake can lower the risk of flares. Managing high blood pressure and diabetes is crucial for avoiding complications.
Reducing uric acid levels prevents flares through lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, increased physical activity, or medication. Identifying gout triggers and avoiding certain foods can also help prevent future attacks.
Drinking enough water daily helps flush out excess uric acid from the body. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet helps reduce the risk of gout.
Importance of Diet in Gout Prevention
To avoid Gout, your diet is critical. Reduce the intake of purine-rich foods like organ meats and increase dairy products to decrease symptoms and uric acid levels. Drinking more water can help your kidneys function and eliminate uric acid. Avoid high-fructose corn syrup, and talk to a doctor before modifying your diet to prevent Gout attacks.
The Role of Regular Exercise
A regular exercise routine can be beneficial in reducing inflammation associated with gout. Physical activity can promote a healthy weight and decrease the risk of gout attacks. Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can also support joint health and improve overall circulation, vital for managing gout. It’s essential to balance exercise and rest to prevent severe symptoms and maintain joint health while managing gout. Additionally, consulting with a healthcare provider or a physical therapist can help design an appropriate exercise regimen that suits individual needs and helps manage gout symptoms effectively.
7. Can Gout Completely Be Cured?
Gout cannot be cured, but lifestyle changes and medication can help manage it. Long-term management is essential to prevent future attacks. Working with a healthcare professional, like a rheumatologist or primary care physician, can help you manage your condition and lower the risk of complications.
To manage gout, maintain a nutritious weight, avoid foods high in purines (red meat, seafood, and alcohol), stay hydrated, and exercise regularly. In addition, medications like NSAIDs, colchicine, and corticosteroids are used to treat gout.
If left untreated or poorly managed, gout can lead to severe complications like joint damage, kidney stones, and chronic kidney disease. Seeking medical attention when experiencing symptoms of a gout attack can help prevent these complications from occurring.
8. What does the number say?
Gout is a prevalent type of arthritis that affects around 8 million Americans. Studies indicate that following the typical American diet can increase the risk of developing gout by 42%, whereas adhering to the DASH diet can help reduce the risk. The prevalence rates of gout vary across different ethnic groups and are more common in developed countries. People with gout are also at a higher risk for other health conditions like kidney disease and cardiovascular disease.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
Is there a link between gout and diet?
Yes, there is a link between gout and diet. Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can increase the risk of gout flare-ups. It is essential to make dietary changes and reduce the intake of purine-rich foods to manage gout effectively.
Does alcohol consumption increase the risk of developing gout?
Yes, alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing gout. It is advisable to limit or avoid alcohol to manage and prevent gout flare-ups.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the causes, symptoms, and available gout treatments is crucial for effectively managing this condition. You can prevent future gout attacks and improve your overall quality of life by making necessary lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medications. However, it is essential to note that while gout can be managed and its symptoms can be relieved, it may not be completely cured. Regular monitoring and follow-up with your healthcare provider are essential to keep your gout under control. Suppose you suspect you have gout or are experiencing symptoms. In that case, it is recommended to consult with a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.